
At UR Medicine, we treat all kinds of bone tumors successfully on a regular basis. Open Med.Not all tumors are cancerous, but even benign tumors can affect your quality of life. Kendoff D, Citak M, Hüfner T et al (2007) Current concepts and applications of computer navigation in orthopedic trauma surgery. Hawi N, Liodakis E, Suero EM et al (2014) Radiological outcome and intraoperative evaluation of a computer-navigation system for femoral nailing: a retrospective cohort study. Krettek Ch, Miclau T, Gru¨n O et al (1998) Intraoperative control of axes, rotation and length in femoral and tibial fractures technical note. Kendoff D, Citak M, Gardner MJ et al (2009) Intraoperative 3D imaging: value and consequences in 248 cases. Ītesok K, Tanaka N, O’Brien A et al (2018) Posttraumatic spinal cord injury without radiographic abnormality. Subburaj K, Ravi B, Agarwal M (2010) Computer-aided methods for assessing lower limb deformities in orthopaedic surgery planning. Jaarsma RL, Pakvis DFM, Verdonschot N et al (2004) Rotational malalignment after intramedullary nailing of femoral fractures. Vaidya R, Dimovski R, Cizmic Z et al (2018) Use of inherent anteversion of an intramedullary nail to avoid malrotation in comminuted femur fractures: a prospective case–control study. Sathy A, Barnwell JC, Shahrestani SN, Moore D (2017) Reliable method for avoiding malrotation deformity after intramedullary nailing of comminuted femur fractures: clinical validation of a previously described technique. Kaiser P, Attal R, Kammerer M et al (2016) Significant differences in femoral torsion values depending on the CT measurement technique. ĭirhold BM, Citak M, Al-Khateeb H et al (2012) Current state of computer-assisted trauma surgery. Ĭao J-Q, Huang J-H, Yuan T et al (2017) Intraoperative correction of femoral rotational deformity using a conventional navigation system and a smartphone: a novel technique. Įl-Menyar A, Muneer M, Samson D et al (2018) Early versus late intramedullary nailing for traumatic femur fracture management: meta-analysis. Stübig T, Min W, Arvani M et al (2012) Accuracy of measurement of femoral anteversion in femoral shaft fractures using a computer imaging software: a cadaveric study. Hawi N, Suero EM, Liodakis E et al (2014) Intra-operative assessment of femoral antetorsion using ISO-C 3D: a cadaver study. Nevertheless, more studies with higher patient numbers, comparison to CT seems to be the next step and can be recommended.

Intraoperative estimation of femoral antetorsion using a 3D C-Arm system and the Linea aspera method seems to be an accurate and feasible method. Specific measurements for different angles did not show any differences between those two utilities. Measurements were then compared in the two methods with a dependent t test.
Cadaver femur break software#
The 3D data set was analyzed using a radiologic software (Visage 7, Visage Imaging Inc, USA). Femur bones were then fractured in a controlled manner and three different internal and external torsion angles were fixed with the help of a Goniometer.

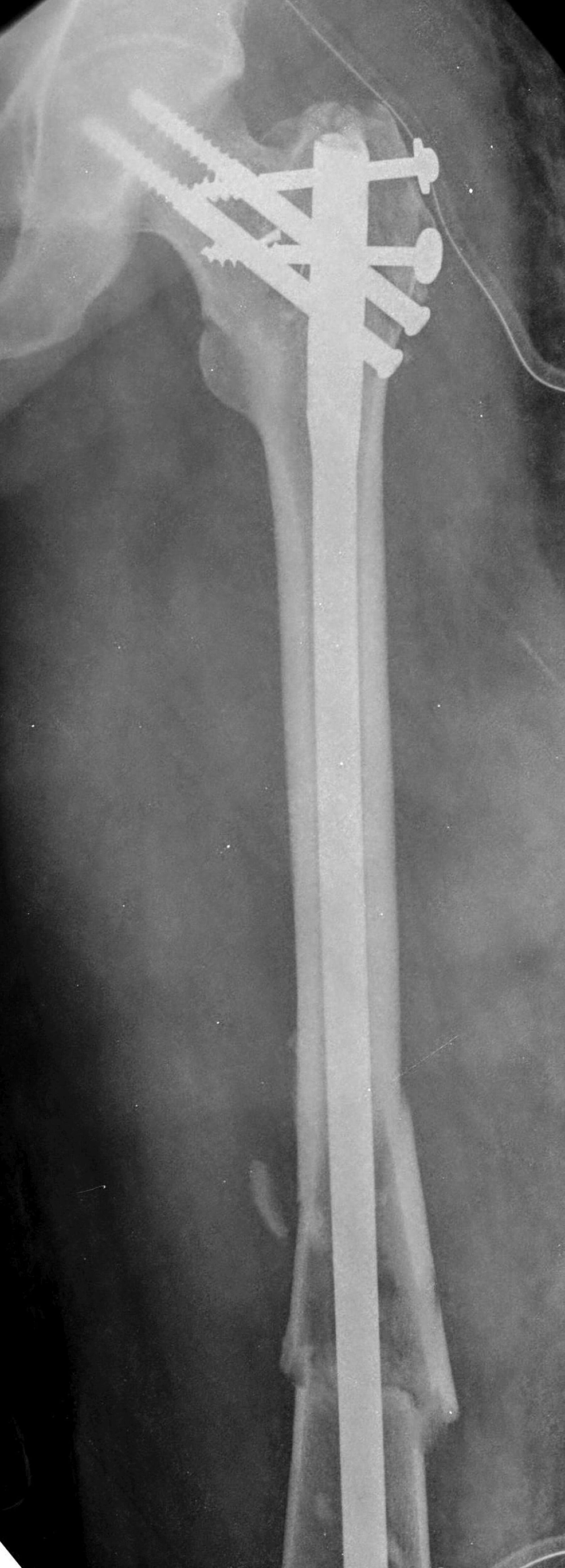
Schanz screws were inserted in the femoral bone in a parallel manner with the help of a fixed drill sleeve. Materials and methodsĪ total of 11 intact femora were used. This study aims to test the accuracy and feasibility of a measurement of femoral torsion of a 3D C-arm system (Linea aspera method) in a cadaver setting.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
